Vision Enhancement and Rehabilitation
Explore the premier vision therapy center in Bhiwani, Haryana, where our optometrists offer top-notch services to improve visual abilities.
- Home
- Service
- Vision Enhancement and Rehabilitation
Overview
Many people labeled as “blind” still have some sight left. Thanks to advances in low vision rehab, they can improve their vision and quality of life. Visual impairment means having uncorrectable reduced vision, not improved by glasses or contacts.
The World Health Organization classifies visual impairment based on the better eye’s vision with the best correction:
- 20/30 to 20/60 is mild vision loss or near-normal vision.
- 20/70 to 20/160 is moderate visual impairment or moderate low vision.
- 20/200 or worse is severe visual impairment or severe low vision.
- 20/500 to 20/1000 is profound visual impairment or profound low vision.
- Less than 20/1000 is near-total visual impairment or near-total low vision.
- No light perception is total visual impairment or total blindness.
There are also classifications based on visual field loss. In the U.S., legal blindness means vision can’t be corrected to better than 20/200 or has 20 degrees or less of remaining visual field.
Visual impairments vary, and just measuring acuity doesn’t predict challenges. Someone with good acuity (20/40) may struggle, while someone with poorer acuity (20/200) may function well in daily tasks.
What causes low vision?
Different eye problems can cause low vision. Here are some common reasons:
- Macular Degeneration:
- Affects the retina at the back of the eye.
- The macula, responsible for sharp central vision, deteriorates.
- It causes blurred vision, difficulty reading, and blind spots.
- Cataracts:
- Clouding of the eye lens.
- Interferes with light reaching the retina.
- Often due to aging, sun exposure, injury, or inherited disorders.
- Surgery can restore vision by replacing the lens.
- Glaucoma:
- Damages the optic nerve due to increased eye pressure.
- Often, there are no early symptoms.
- It can lead to peripheral vision defects and night vision issues.
- Treatable with drugs or surgery if detected early.
- Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Affects people with diabetes.
- Causes abnormal blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems.
- Regulating blood sugar is crucial for treatment.
- Retinitis Pigmentosa:
- An inherited disease that gradually impairs night and side vision.
- Typically, it begins with night blindness in childhood.
- Amblyopia:
- Results from abnormal childhood visual development.
- It causes blurry vision that is not easily corrected with glasses.
- Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP):
- It affects premature infants due to high oxygen levels.
- It can lead to vision issues if not managed.
- Retinal Detachment:
- The retina separates from its underlying layer.
- Causes total vision loss in the affected eye.
- Early diagnosis allows surgical reattachment.
- Acquired (Traumatic) Brain Injury:
- Head injuries, brain damage, or stroke can damage vision.
- Symptoms include reduced visual acuity, blurred vision, and difficulty performing visual tasks.
Common types of low vision
There are different types of low vision:
- Loss of Central Vision:
- Creates a blur or blind spot in the centre.
- It makes reading, recognizing faces, or seeing details far away hard.
- Side vision is usually fine, so moving around is not affected.
- Loss of Peripheral (Side) Vision:
- Unable to see to the sides or above and below eye level.
- Central vision remains, allowing seeing ahead, reading, and recognizing faces.
- It is often called “tunnel vision” and can impact mobility.
- Blurred Vision:
- Both near and far vision are out of focus.
- Even with glasses, things appear blurry.
- Reduced Contrast Sensitivity:
- Resulting in a loss of vision quality.
- People might feel like there’s a general haziness or cloudiness.
- Glare Light Sensitivity:
- Standard levels of light cause discomfort.
- Creates a washed-out or glaring image, especially in bright light.
- Night Blindness:
- Inability to see well in low-light conditions.
- Difficulty seeing outside at night or in dimly lit places.
Low vision care
Some eye doctors specialize in helping people with low vision. They examine and assist patients with visual impairments.
These doctors create a unique plan for each type of vision problem after a thorough examination. The plan may include glasses, magnification devices, and other tools to maximize vision.
This vision rehabilitation aims to help patients reach their visual goals and improve their quality of life. The plan may involve various options, such as glasses, magnifiers, and technology to control glare. Patients also get support from other professionals like teachers, psychologists, and occupational therapists to enhance their overall well-being.
Low vision exam
A special eye doctor will ask about your health and family history during a low-vision exam. They focus on how vision problems affect daily activities like reading, computer use, or recognizing faces. They also check for signs of feeling down, which can happen with vision loss. The doctor does detailed tests for each eye, measuring your vision using unique charts designed for low vision. They also check things like glare, contrast sensitivity, and reading ability. After the exam, the doctor creates a personalized plan to help improve your vision, which might involve several clinic visits.
Low vision devices
People with low vision can enhance their independence and safety through various rehabilitation options. These options significantly improve their quality of life. Many individuals with low vision could benefit from these treatments, but unfortunately, only about 20 to 25% of them have visited a low-vision eye doctor.
Here are some commonly recommended devices:
- Spectacle-Mounted Magnifiers:
- Magnifying lenses in glasses or on a unique headband.
- Leaves hands free for tasks like reading.
- Handheld or Spectacle-Mounted Telescopes:
- Mini telescopes for seeing at a distance or reading.
- Bioptic telescopes can be used for driving in some states.
- Handheld and Stand Magnifiers:
- Optical magnifiers for quick reading of labels or price tags.
- Some come with built-in lights.
- Electronic (Video) Magnification:
- Portable, tabletop, or head-mounted systems for magnifying images.
- Allows variable levels of magnification, brightness, and contrast adjustment.
- Assistive Technology:
- Features on smartphones and computers for accessibility.
- Screen readers, speech output, and software enlargement programs for full technology access.
Low vision rehabilitation
If you or someone you know has trouble seeing, you must ask your eye doctor about low vision rehabilitation. This kind of care is the standard for helping people with vision loss. A doctor of optometry who offers low-vision rehabilitation can assist in regaining independence and improving the quality of life.
In these rehabilitation programs, people with low vision can learn helpful techniques for daily activities. Government and private programs offer counseling, occupational therapy, and training to support their needs.
Since 1999, the American Optometric Association and the American Academy of Ophthalmology have suggested that Medicare cover low-vision rehabilitation services. Some Medicare carriers now have policies covering these services. To know more, check with your eye doctor’s office about this coverage.
Our Related Services
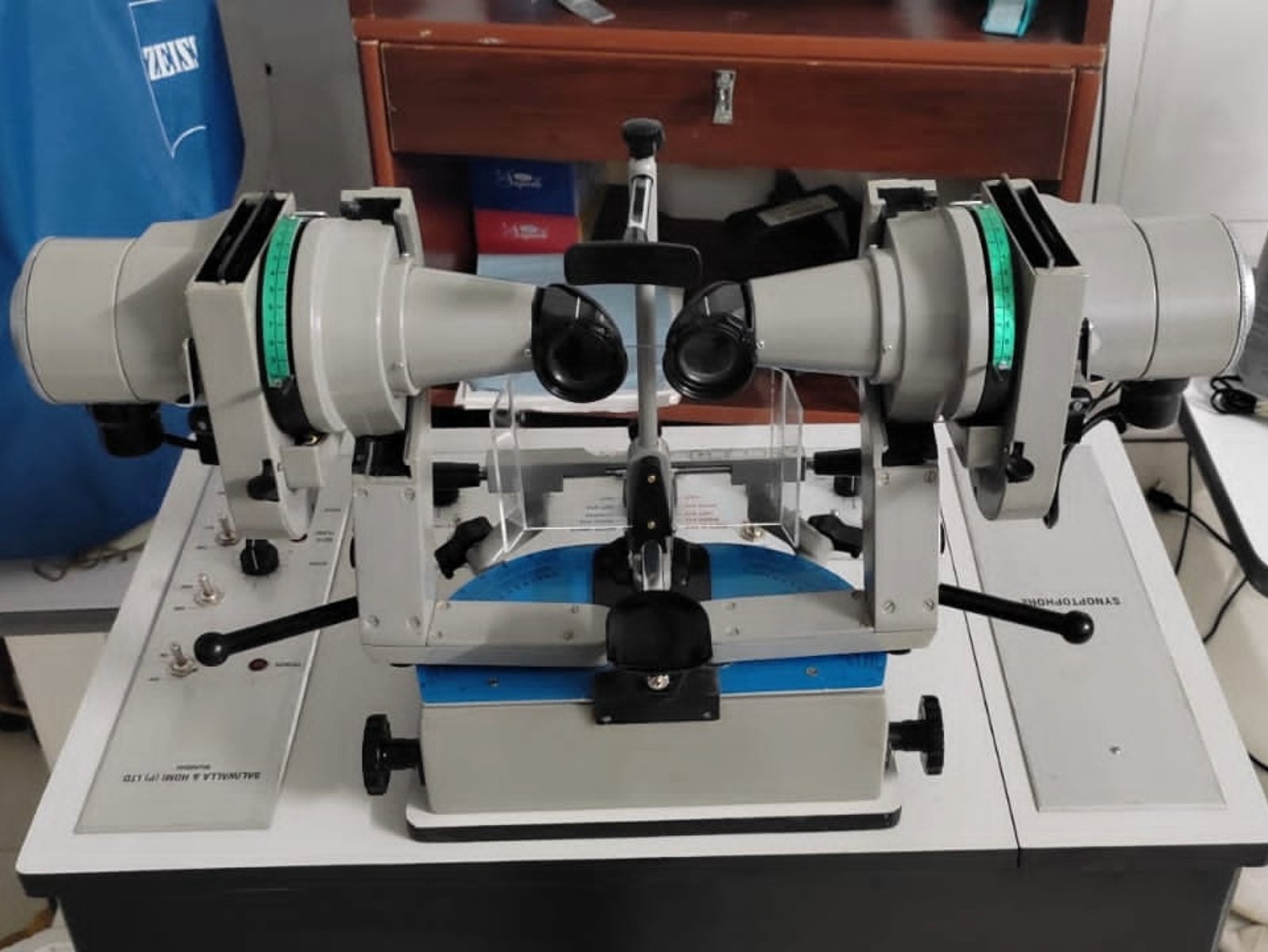
Binocular Vision and Orthoptic
Get the best eye hospital in India for Binocular vision and orthoptics treatment without any difficulty at Dhir hospitals in Bhiwani, Haryana.

Dry Eye
Visit the leading vision therapy and rehabilitation centre in Bhiwani, Haryana. Our optometrists provide the best services to enhance visual abilities.
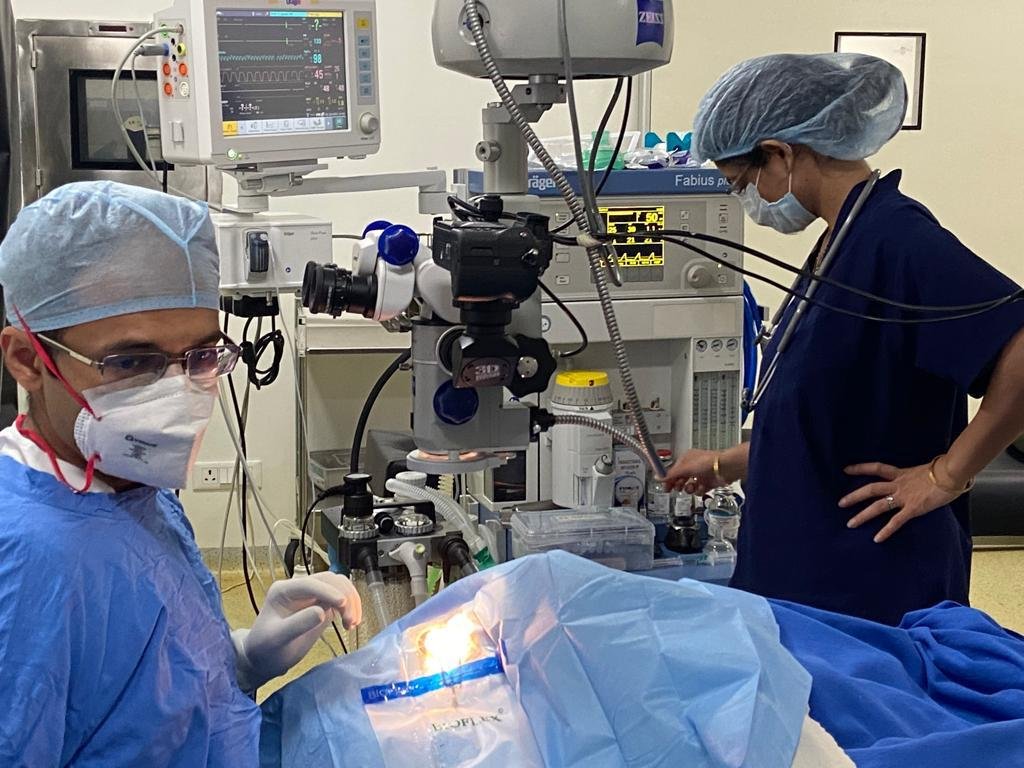
Modular OT & Anaesthesia Facility
Experience Latest modular OT and anesthesia facilities at Dhir Hospital. Our advanced infrastructure ensures a safe and efficient surgical environment.
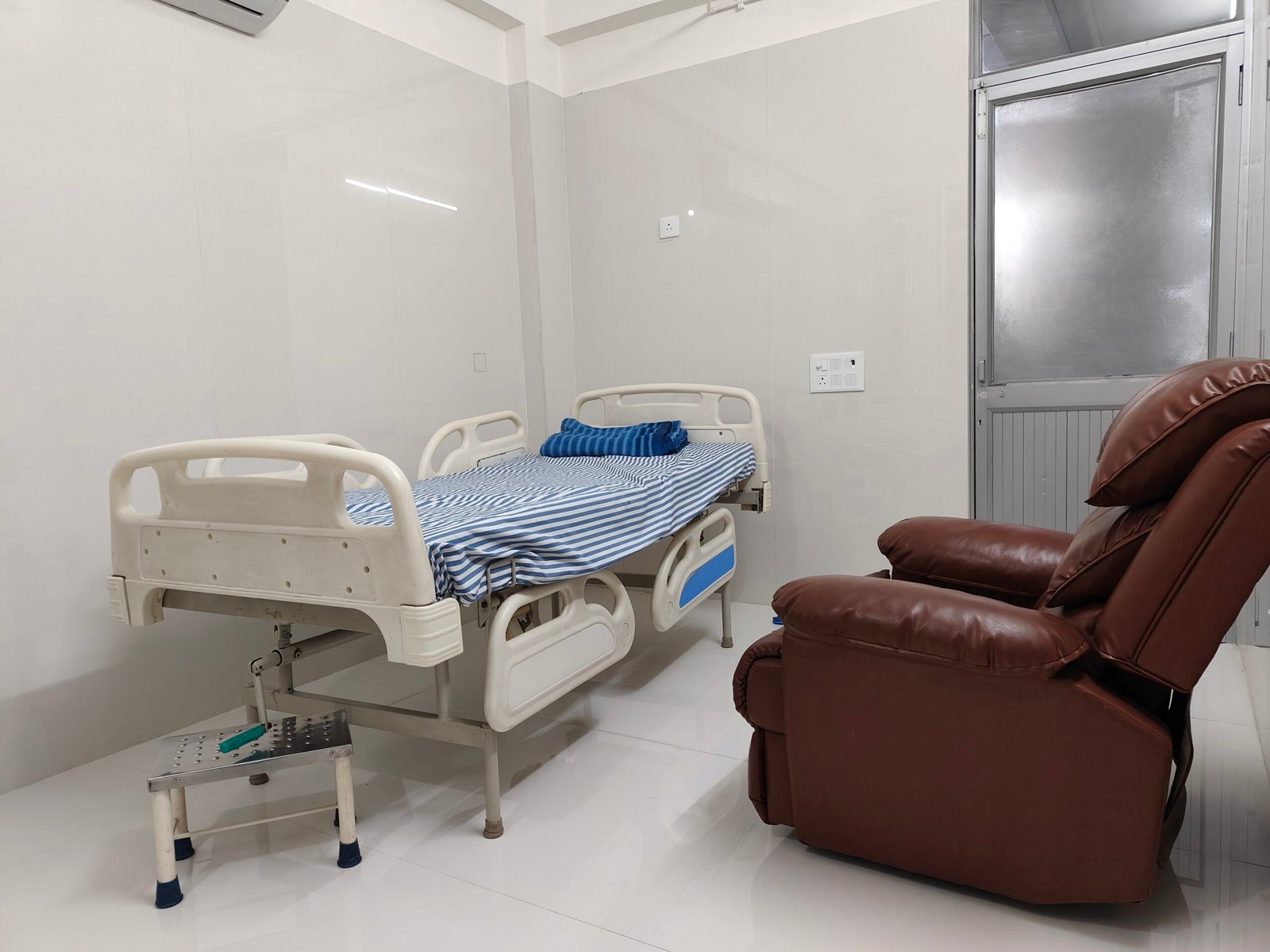
OPD & Private Room
Experience personalized care and comfort at Dhir Hospital with our OPD and private room facilities. Our dedicated team of doctors and staff ensure a seamless healthcare experience.
FAQ
Frequently Ask Questions.
Vision enhancement and rehabilitation refer to a range of techniques, therapies, and technologies aimed at improving visual function and helping individuals with visual impairments regain or enhance their ability to see. These approaches can include visual aids, assistive devices, training programs, and surgical interventions.
Vision enhancement and rehabilitation can benefit individuals with various visual impairments, such as low vision, cataracts, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and glaucoma, among others. It can be helpful for people of all ages, from children to older adults, who are experiencing difficulties with their vision.
There are several techniques and interventions used in vision enhancement and rehabilitation. Some common methods include the use of magnifying lenses, optical aids, and electronic devices to improve visual acuity. Visual training programs and exercises can also help individuals improve their visual processing, spatial awareness, and eye-hand coordination. In some cases, surgical procedures may be recommended to address specific eye conditions.





